
一、研究背景
硅(Si)基负极材料因其数倍于传统石墨材料的高理论比容量和接近的工作电压而被广泛认为是下一代高比能锂离子电池负极材料的选择之一。然而,硅基负极材料的大规模应用仍然存在着挑战。在电化学充放电循环过程中硅基负极材料活性物质与电解液之间的寄生界面副反应严重,结合其大的相对体积变化,导致硅基负极界面结构不稳定以及容量迅速衰减;在首次锂化过程中,有机电解液在Si表面发生的副反应尤其严重,该过程消耗了相当量的电解液与活性锂,导致首次库伦效率(ICE)较低。尽管材料结构设计、复合化和电解液工程在改善硅基负极的综合电化学性能上取得了很多进展,但当前硅基负极的ICE依然偏低,成为限制其广泛应用的因素之一。因此,探索行之有效的方法减少硅基负极初始锂损耗、提高ICE极为重要。
二、成果简介
近日,华中科技大学孙永明教授等在国际期刊Applied Physics Letters上发表了题为“Double-shell interphase design enabling suppressed side reactions for stable Si battery anode”的研究论文。该论文提出一种功能性界面结构设计思路:通过改变活性物质的界面反应活性,调控活性物质与电解液之间的反应、减少电解液与活性锂在电化学锂化/去锂化过程中的无效消耗、从而有效提高硅基负极材料的ICE。作为例证,该研究报道了一种内部VO2纳米层与外部C纳米层组成的双壳层界面结构(VO2@C)。在首次电化学电化学锂化/去锂化过程中,该结构能有效抑制界面副反应,促进界面富LiF的无机固态电解质界面(SEI)的生成,提高硅基负极的首次库伦效率(达到90.2%)和电化学循环稳定性。与商业石墨混合制备出的混合负极展现出了高的可逆比容量(596 mAh g-1)和面容量(3.46 mAh cm-2),并实现了优异的电化学循环稳定性(100次循环容量保持率为83.8%)。该实验验证了调控活性材料与电解液之间反应性对改善硅基材料ICE的有效性,为提高硅基负极材料性能提供了新思路。
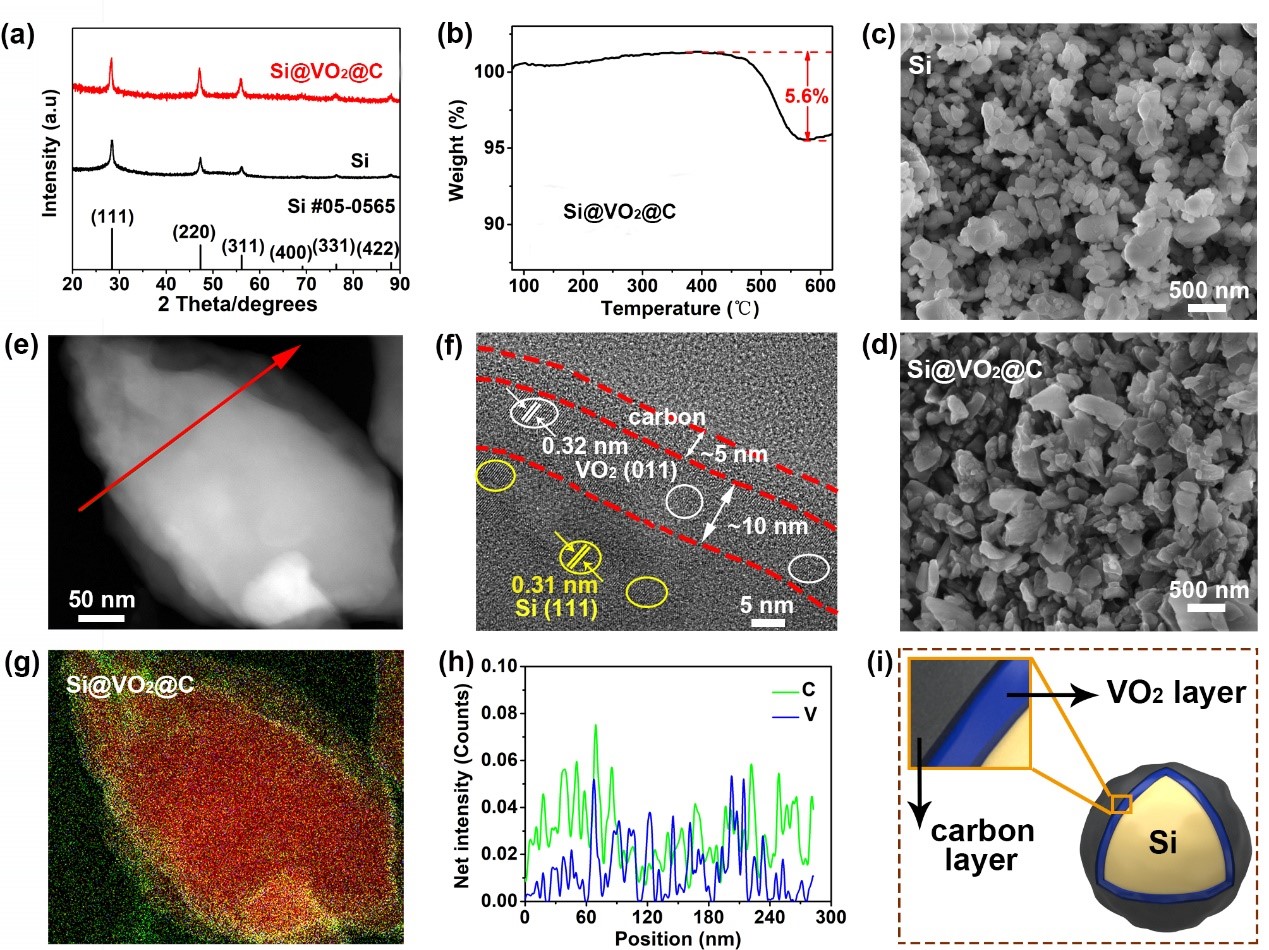
Figure 1. Characterizations of the pristine Si and Si@VO2@C. (a) XRD patterns of the pristine Si (bottom) and Si@VO2@C (top). (b) TG curve of Si@VO2@C. SEM images of (c) the pristine Si and (d) Si@VO2@C. (e) Dark-field TEM image and (g) the corresponding EDS mapping image of Si@VO2@C. Green, yellow, and red stand for C, V and Si, respectively. (f) High-resolution TEM image of Si@VO2@C. (h) EDS count-position plot across the particle in (e). (i) Schematic of the double-shell interphase structure of Si@VO2@C
要点
1. 利用机械球磨结合高温处理工艺制备了具有双壳层结构的Si@VO2@C。制备所得的Si@VO2@C材料,内部VO2致密纳米层厚度约为10 nm,主要作用是隔绝Si与电解液的直接接触;外部C纳米层厚度约为5 nm,主要作用为固定内部VO2纳米层并提高材料的电子电导。
2.制备所得的Si@VO2@C材料,内部VO2致密纳米层厚度约为10 nm,主要作用是隔绝Si与电解液的直接接触;外部C纳米层厚度约为5 nm,主要作用为固定内部VO2纳米层并提高材料的电子电导。
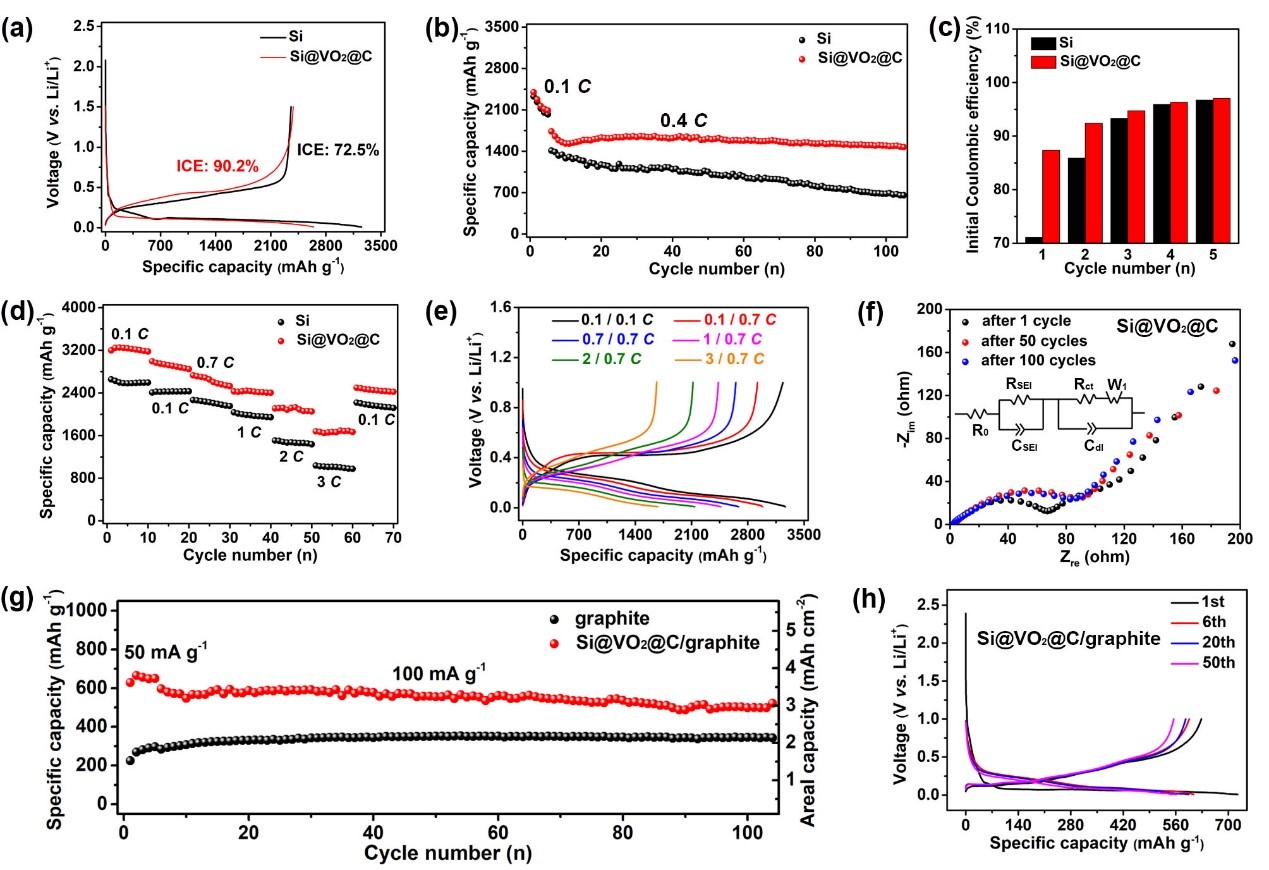
Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of Si@VO2@C. (a) The initial voltage-capacity profiles of pristine Si (black) and Si@VO2@C (red) electrodes. (b) Electrochemical cycling performance of pristine Si (black) and Si@VO2@C (red) electrodes at 0.4 C. (The electrodes were first activated at 0.1 C for five cycles before long-term cycling.) (c) Coulombic efficiency of pristine Si (black) and Si@VO2@C (red) electrodes for the initial five cycles. (d) Rate performance of pristine Si (black) and Si@VO2@C (red) electrodes at different C rates and (e) the corresponding voltage-capacity profiles of Si@VO2@C electrode. (f) Nyquist plots of the Si@VO2@C electrode after 1 (black), 50 (red), and 100 (blue) cycles and the equivalent circuit (insert). (g) Electrochemical cycling performance of the hybrid Si@VO2@C/graphite and bare graphite electrodes at 100 mA g-1 and (h) the corresponding voltage-capacity profiles of the hybrid Si@VO2@C/graphite electrodes for the selected cycles
要点
1. Si@VO2@C极片的首次库伦效率为90.2%,比纯纳米Si极片的首次库伦效率高18%。
2. Si@VO2@C极片在0.4 C(1 C= 2000 mA g-1)的电流密度下,循环100圈的容量保持率为84.8%,展现了良好的循环性能。
3.电化学阻抗图(EIS)中,Si@VO2@C极片循环50圈和100圈的阻抗没有明显变化,说明Si@VO2@C在电化学循环过程中保持稳定的界面结构。
4.Si@VO2@C/graphite混合电极具有高的可逆比容量596 mAh g-1和面容量3.46 mAh cm-2,且循环100圈后容量保持率为83.8%,展现了良好的电化学循环稳定性。