
一、研究背景
金属锂比容量高(3860 mAh g-1)、工作电位低(与标准氢电极相比为-3.04 V),是一种极具应用前景的高比能二次电池负极材料。然而,较差的循环稳定性阻碍了其实际应用。由于金属锂高的反应活性及充放电过程中大的体积变化,金属锂负极与电解液持续发生副反应,造成活性锂和电解液的不断消耗,并伴随着锂枝晶和死锂的形成及电极的粉化。研究表明在金属锂负极表面构筑氟化界面能有效抑制电极/电解液之间的反应,进而提高金属锂负极的电化学稳定性,助力实现稳定的高比能锂金属电池。
二、成果简介
近日,华中科技大学孙永明教授课题组设计了一种富氟化锂(LiF)锂金属复合负极,揭示了LiF溶解-再沉淀的Li金属界面保护机制,动态构筑了稳定致密的金属锂氟化界面,实现了薄锂金属负极的长循环寿命和高库伦效率。所实现的氟化界面不仅能抑制电极与电解液的副反应,还能促使金属锂在电极表面发生平面沉积行为,实现了稳定的电极结构,提升了金属锂负极的循环稳定性,该种构筑稳定氟化界面机制在概念上不同于所报道的其他机制(图1a)。利用了氟化锡(SnF2)与金属Li之间的自发反应,通过将二者反复机械揉和,制备出Li/Li22Sn5/LiF复合锂金属负极。LiF超细纳米颗粒在该电极中均匀分布。LiF微溶于碳酸酯类电解液溶剂(例如碳酸乙烯酯和氟代碳酸乙烯酯),其溶解-沉淀平衡能使其在金属锂活性表面动态析出,帮助构筑富含LiF 的固态电解质界面(SEI)。此外,复合电极中高离子/电子导电率的Li22Sn5合金骨架,有助于加快载流子的传输,抑制锂枝晶的形成。所制备的Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极表现出优异的电化学性能:在1 mA cm-2和1 mAh cm-2的条件下,Li/Li22Sn5/LiF复合电极在碳酸酯类电解液中50次循环的平均库仑效率高达99.2%,而在相同测试条件下纯Li电极仅为96%。在1 mA cm-2和2 mAh cm-2条件下,Li/Li22Sn5/LiF对称电池的循环寿命超过1600小时,远远高于纯Li电极的300小时。使用超薄厚度(80 μm)的复合负极匹配面容量为4.0 mAh cm-2的LiCoO2正极组装了低负极活性物质面容量/正极活性物质面容量比(N/P比为2:1)的全电池,在0.5 C充放电倍率和宽的工作电压(2.8-4.5 V)区间内展现出高容量和高稳定性(100次循环的容量保持率高达91.1%)。
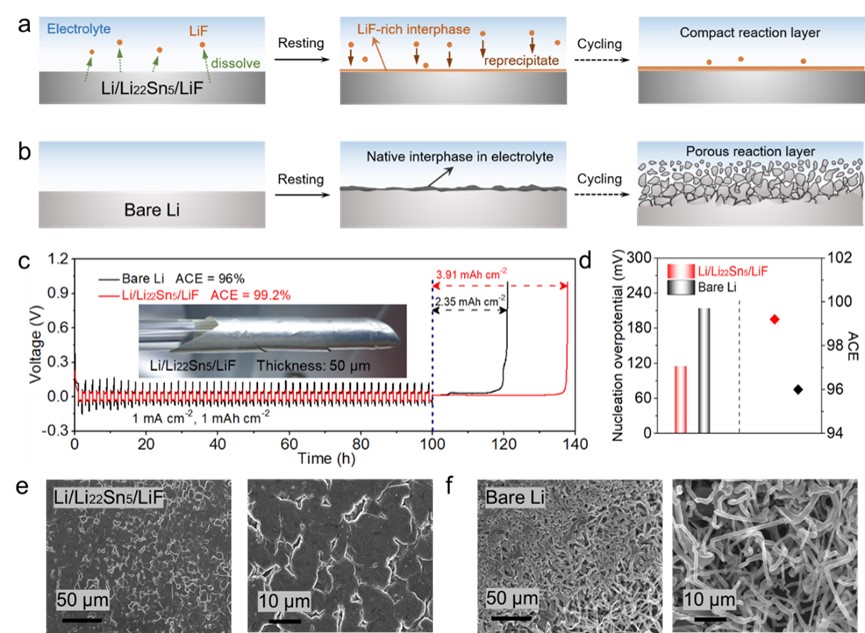
图1. (a) Schematic of LiF dissolution-reprecipitation mechanism-enabled interphase protection for Li/Li22Sn5/LiF electrode on cycling. (b) Schematic for the evolution of bare Li electrode on cycling. (c) Li plating/stripping voltage profile of Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and bare Li electrodes at 1 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2 for 50 cycles and subsequent Li stripping at 0.2 mA cm-2. The inset shows a digital image of 50 µm-thick Li/Li22Sn5/LiF foil. (d) Comparison of nucleation overpotential and ACE of Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and bare Li electrodes. Top-view SEM images of (e) Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (f) bare Li electrodes after electrochemical plating of metallic Li at 1 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2.
要点
1. 氟化界面能抑制电极与电解液的副反应,提升电极的循环稳定性。在1 mA cm-2和1 mAh cm-2的条件下Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极50次循环的平均库伦效率高达99.2%,而纯Li负极仅为96%。
2. 氟化界面能促使金属Li在Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极表面发生平面大尺度颗粒沉积。
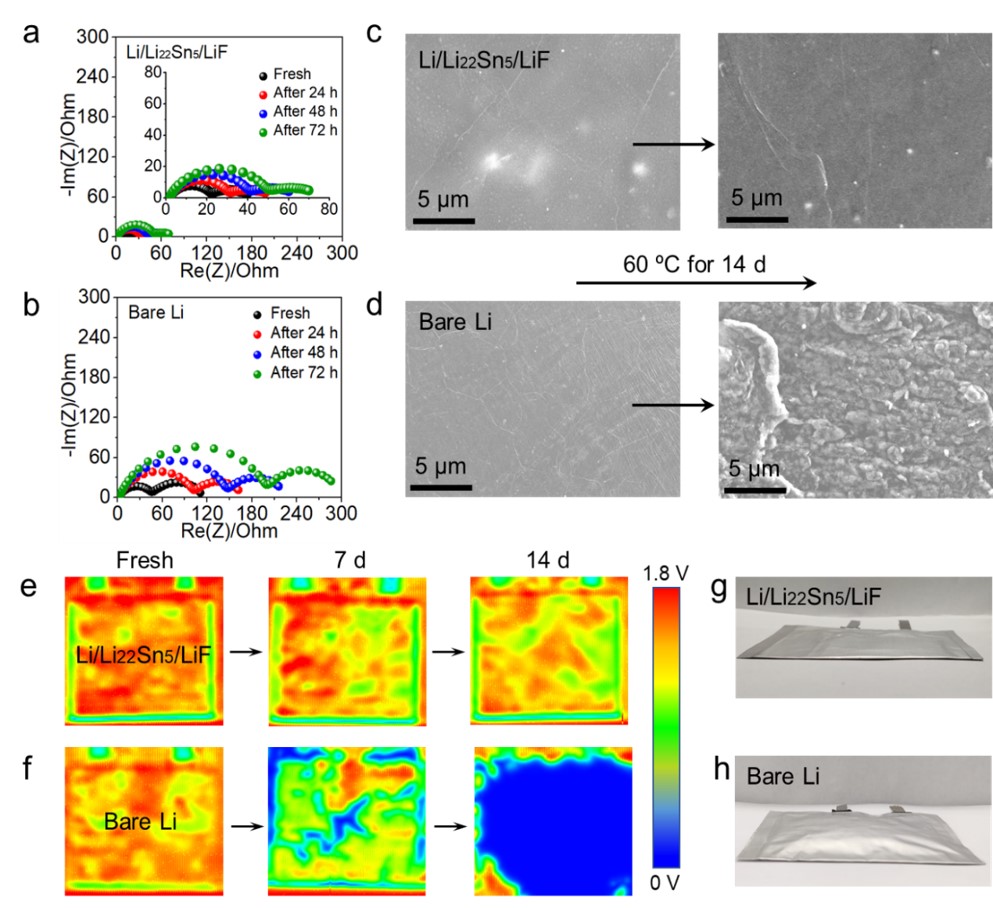
Figure 2. Nyquist plots of (a) Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (b) bare Li symmetric cells after resting at 60 °C for different times. SEM images of (c) fresh Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (d) bare Li samples before and after resting in electrolyte at 60 °C for 14 d. Ultrasonic transmission mappings of (e) Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (f) bare Li symmetric pouch cells during resting at 60 °C. Optical photograph of (g) Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (h) bare Li symmetric pouch cells after resting at 60 °C for 14 d. The size of electrodes used in pouch cells is 4 × 5 cm. Gas evolution is observed for the bare Li symmetric pouch cells.
要点
1. 氟化界面能缓解电极界面阻抗的增加,抑制电解液对电极的腐蚀。60 ℃条件下静置时,复合电极的界面阻抗仅从20 Ω增加到50 Ω,而纯Li电极的界面阻抗从60 Ω增加到210 Ω。
2. 氟化界面能抑制软包电池的产气行为。
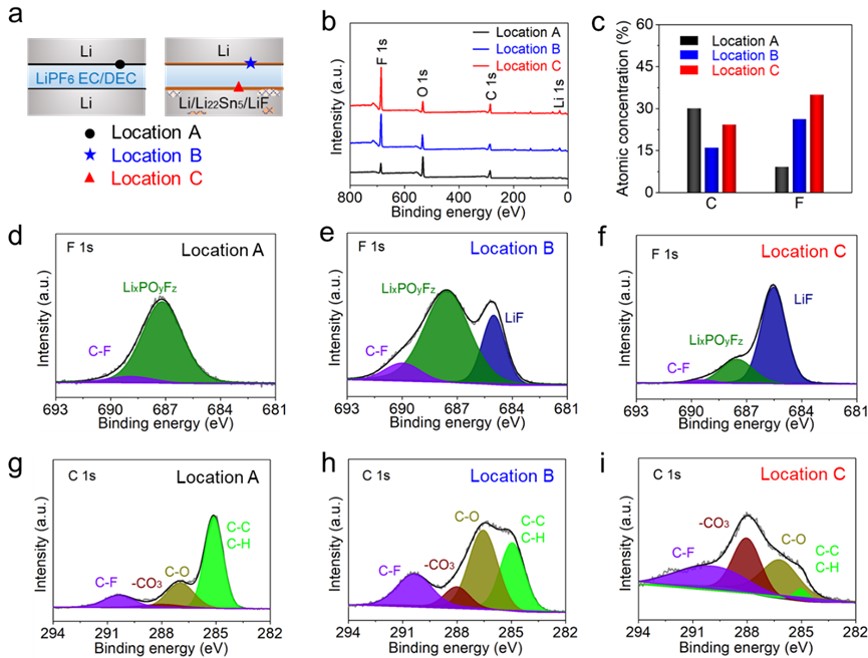
Figure 3. (a) Illustrations of Li||Li cell (left) and Li/Li22Sn5/LiF||Li cell (right). Location A on a Li electrode surface of Li||Li cell, location B on Li electrode surface, and location C on the Li/Li22Sn5/LiF electrode surface of Li/Li22Sn5/LiF||Li cell are labeled and selected for XPS measurement after resting. (b) XPS survey spectra obtained at locations A, B, and C. (c) Atomic concentrations of C and F at the three locations according to XPS results. High-resolution XPS spectra of F 1s and C 1s obtained at locations (d, g) A, (e, h) B, and (f, i) C.
要点
1. LiF的溶解-沉淀能使其在金属锂活性表面动态析出,并参与在金属锂电极表面原位构筑富含LiF 的SEI。
2. 氟化界面能减少电极表面SEI中有机组分的含量。
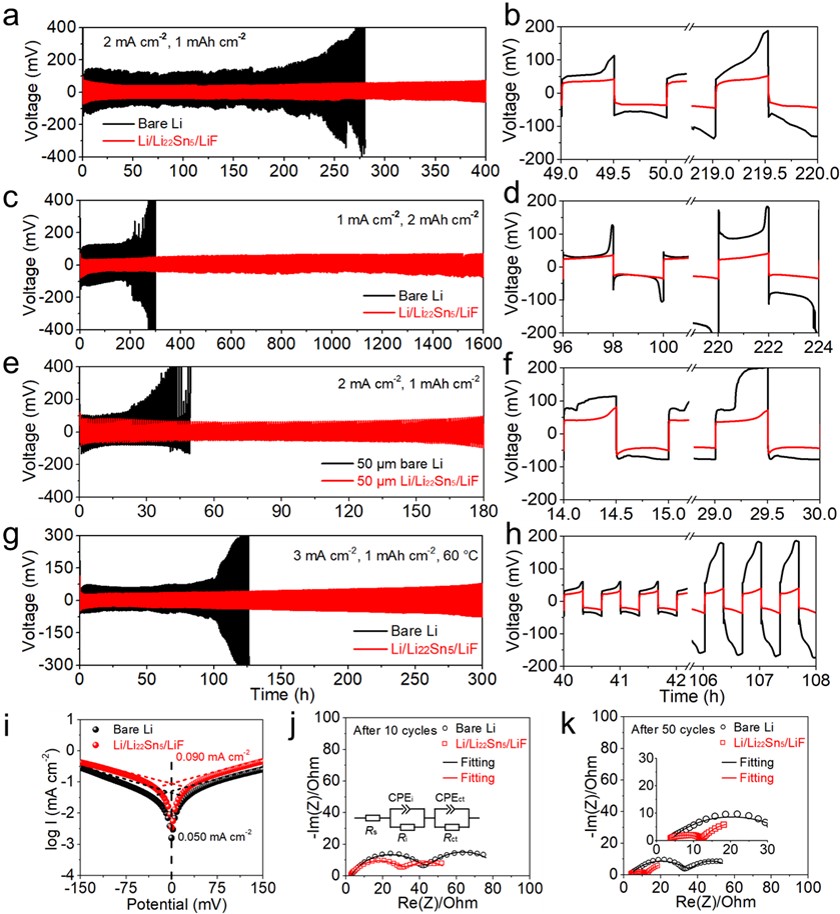
Figure 4. The comparison of electrochemical cycling performance and the corresponding enlarged voltage profiles at selected times for Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and bare Li symmetric cells at (a, b) 2 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2, (c, d) 1 mA cm−2 and 2 mAh cm−2, (e, f) 2 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2 for 50 µm-thick electrodes, (g, h) 3 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2 at 60 °C. (i) Tafel curves of bare Li and Li/Li22Sn5/LiF symmetric cells. Impedance spectra of bare Li and Li/Li22Sn5/LiF symmetric cells after (j) 10 cycles and (k) 50 cycles at 1 mA cm−2 and 1 mAh cm−2. The inset in Fig. 4j showed the used equivalent circuit model.
要点
1. Li/Li22Sn5/LiF对称电池在1 mA cm−2和2 mAh cm-2的条件下能稳定循环1600 h,且过电位小于25 mV,展现了良好的循环稳定性。
2. 塔菲尔曲线中,Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极的交换电流密度为0.090 mA cm-2,而纯Li的仅为0.050 mA cm-2,表明Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极反应动力学更快。
3. 电化学阻抗图(EIS)中,Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电极循环10圈和50圈的界面阻抗和传质阻抗均比纯Li电极小,展现出更好的界面稳定性以及更快的Li沉积-溶解行为。
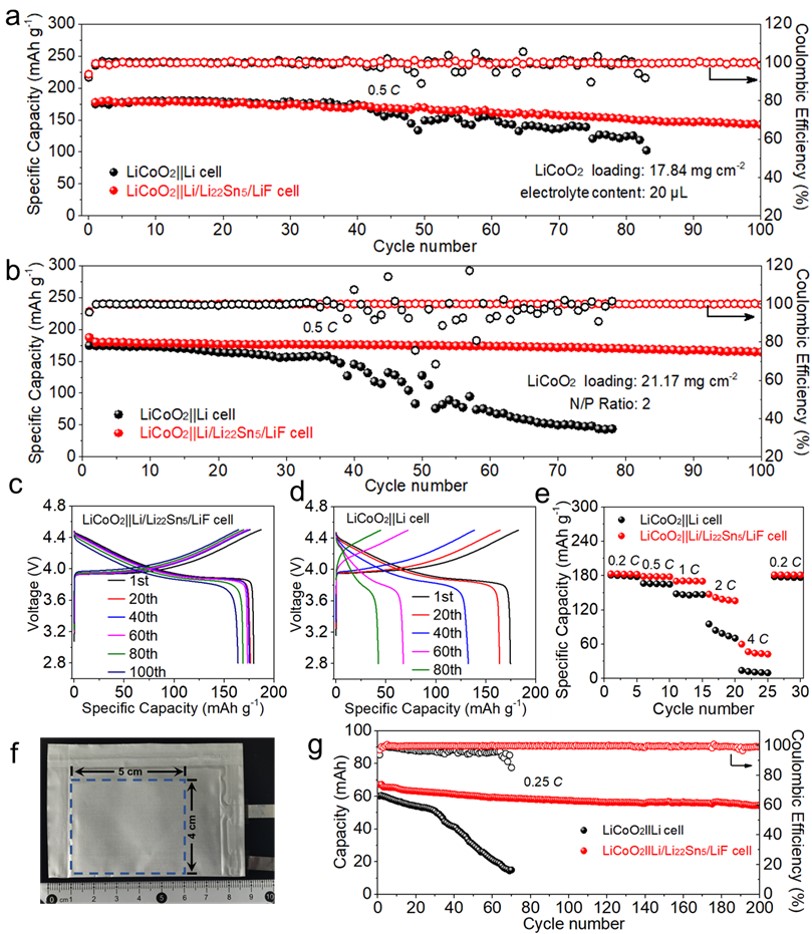
Figure 5. Cycling performance of LiCoO2||Li and LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF full cells at 0.5 C (a) with 20 µL electrolyte, (b) with low N/P ratio of 2:1. Voltage profiles of (c) LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF and (d) LiCoO2||Li cells for selected cycles in Fig. 5b. (e) Rate capability of LiCoO2||Li and LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF full cells. (f) Optical image of a LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF double-side-electrode pouch cell. (f) Cycling performance of LiCoO2||Li and LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF double-side-electrode pouch cells at 0.25 C.
要点
1. 使用80 μm的Li/Li22Sn5/LiF复合负极匹配面容量为4.0 mAh cm-2的LiCoO2正极组装的N/P比为2:1的全电池,在0.5 C充放电倍率和宽的工作电压(2.8-4.5 V)区间内展现出高容量和高稳定性(100次循环的容量保持率高达91.1%),说明Li/Li22Sn5/LiF在电化学循环过程中保持稳定的电极结构。
2. LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电池在2 C充放电倍率下依然保持150 mAh g-1的比容量,展现了良好的倍率性能。
3. 容量为70 mAh的LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF软包电池0.25 C充放电倍率循环200次的容量保持率为83.6%。LiCoO2||Li/Li22Sn5/LiF电池在2 C充放电倍率下依然保持150 mAh g-1的比容量,展现了良好的倍率性能。